MDL(Metadata Lock)中所有的MDL_lock都是存在一个全局的Hash表当中,MySQL使用的是LF_HASH
【版本:mysql-8.0.13】
LF_HASH的实现主要在下面几个文件中:
1. include/lf.h
2. mysys/lf_dynarray.cc
3. mysys/lf_alloc-pin.cc
3. mysys/lf_hash.cc
lf_dynarray.cc定义了LF_DYNARRAY,它是一个可以多级的、可动态扩充的数组,最多支持4311810304元素
lf_alloc_pin.cc定义了LF_PINS,LF_PINBOX和LF_ALLOCATOR,本篇详细说明
lf_hash.cc集合上面定义的东西,实现了一个Lock-Free Extensible Hash Tables
本篇先主要介绍下LF_DYNARRAY,LF_PINS,LF_PINBOX和LF_ALLOCATOR,后面再单独一篇介绍LF_HASH
先上图:
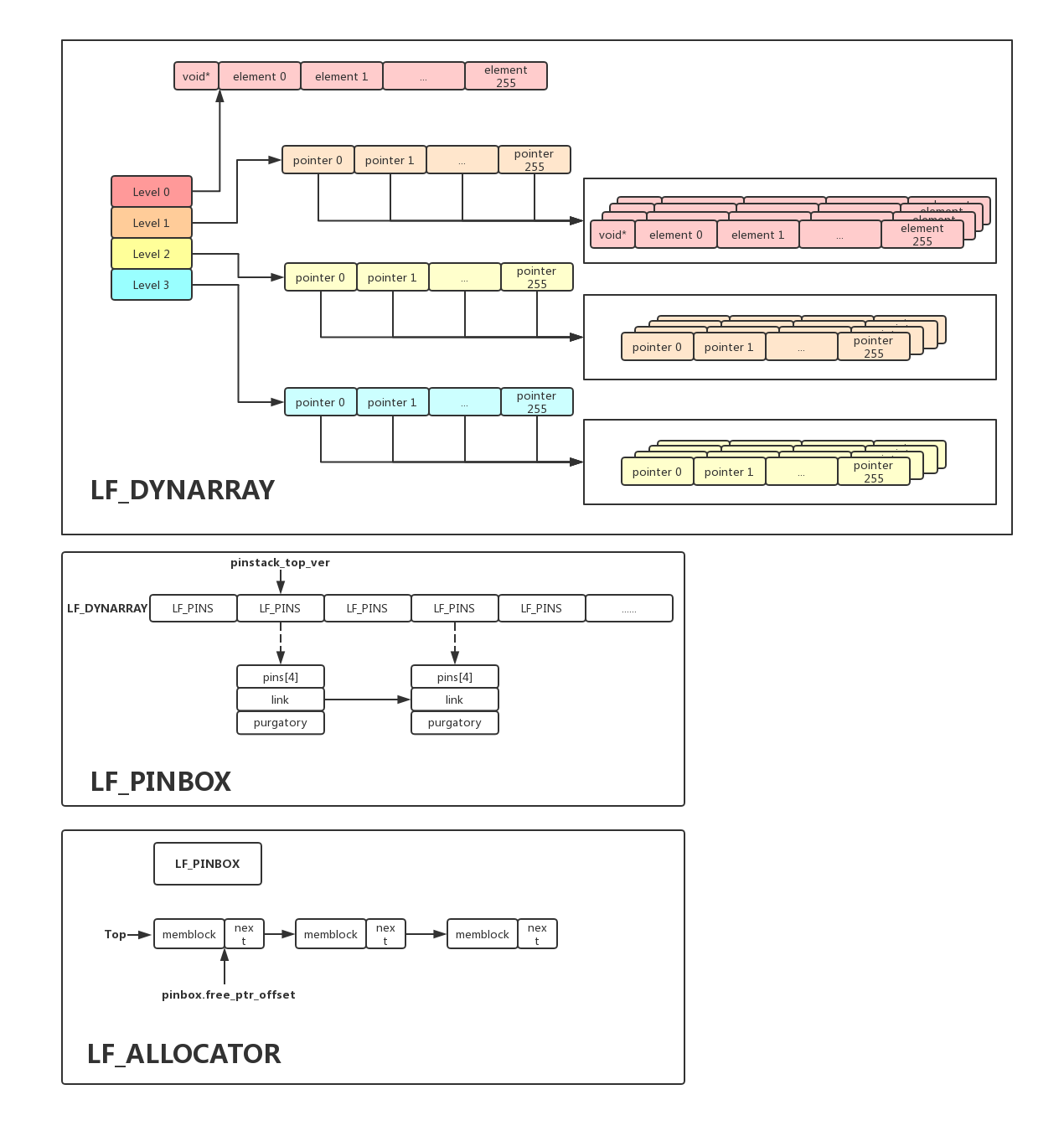
1. LF_DYNARRAY
#define LF_DYNARRAY_LEVEL_LENGTH 256
#define LF_DYNARRAY_LEVELS 4
typedef struct {
std::atomic<void *> level[LF_DYNARRAY_LEVELS];
uint size_of_element;
} LF_DYNARRAY;
它的定义很简单,分为4级:
level[0]:一个包含256个元素的数组,其中每个元素大小为size_of_element
level[1]:一个包含256个指针的数组,其中每个指针指向1一个同level[0]定义的数组
level[2]:一个包含256个指针的数组,其中每个指针指向1一个同level[1]定义的数组
level[3]:一个包含256个指针的数组,其中每个指针指向1一个同level[2]定义的数组
通过这样递归的定义,可以实现一个容量很大,但不要求连续内存的数组,通过lf_dynarray_lvalue函数来获取指定idx位置元素的地址进行访问,它是LF_DYNARRAY中最关键的函数:
/*
Returns a valid lvalue pointer to the element number 'idx'.
Allocates memory if necessary.
*/
void *lf_dynarray_lvalue(LF_DYNARRAY *array, uint idx) {
void *ptr;
int i;
// 这里先定位idx在哪一个level,比如如果小于256,那一定在level[0],如果大于256,小于65792
// 那就在level[1]
// ......
for (i = LF_DYNARRAY_LEVELS - 1; idx < dynarray_idxes_in_prev_levels[i]; i--)
/* no-op */;
// 将level[i]数组的基址赋值给ptr_ptr
std::atomic<void *> *ptr_ptr = &array->level[i];
// idx减去本level之前所有levels的容量总和,得到在本level中的idx
idx -= dynarray_idxes_in_prev_levels[i];
// 当确定了level之后,下面这个for循环主要就是逐级检查、申请内存
// 最终定位到最小的那一级的idx
for (; i > 0; i--) {
if (!(ptr = *ptr_ptr)) {
void *alloc = my_malloc(key_memory_lf_dynarray,
LF_DYNARRAY_LEVEL_LENGTH * sizeof(void *),
MYF(MY_WME | MY_ZEROFILL));
if (unlikely(!alloc)) {
return (NULL);
}
if (atomic_compare_exchange_strong(ptr_ptr, &ptr, alloc)) {
ptr = alloc;
} else {
my_free(alloc);
}
}
ptr_ptr =
((std::atomic<void *> *)ptr) + idx / dynarray_idxes_in_prev_level[i];
idx %= dynarray_idxes_in_prev_level[i];
}
// 此时idx已经确定到256之内,检查最小的这一级对应的array
// 是否已经申请,没有的话则申请一个
if (!(ptr = *ptr_ptr)) {
uchar *alloc, *data;
alloc = static_cast<uchar *>(
// 注意这里除了size_of_element之外,还多申请一个
// 指针大小
my_malloc(key_memory_lf_dynarray,
LF_DYNARRAY_LEVEL_LENGTH * array->size_of_element +
MY_MAX(array->size_of_element, sizeof(void *)),
MYF(MY_WME | MY_ZEROFILL)));
if (unlikely(!alloc)) {
return (NULL);
}
/* reserve the space for free() address */
data = alloc + sizeof(void *);
{
/* alignment */
intptr mod = ((intptr)data) % array->size_of_element;
if (mod) {
data += array->size_of_element - mod;
}
}
// 数组基址之前是指向这块内存的首址
((void **)data)[-1] = alloc; /* free() will need the original pointer */
if (atomic_compare_exchange_strong(ptr_ptr, &ptr,
static_cast<void *>(data))) {
ptr = data;
} else {
my_free(alloc);
}
}
return ((uchar *)ptr) + array->size_of_element * idx;
}
2.2 ABA Problem
我们通常通过CAS loops来实现Lock free,但这有可能引入ABA问题,举个例子,下面是一个Lock free stack:
/* Naive lock-free stack which suffers from ABA problem.*/
class Stack {
std::atomic<Obj*> top_ptr;
//
// Pops the top object and returns a pointer to it.
//
Obj* Pop() {
while(1) {
// 获取栈顶指针top_ptr, 赋值给ret_ptr
Obj* ret_ptr = top_ptr;
if (!ret_ptr) return nullptr;
// 获取栈顶的下一个元素指针next_ptr
Obj* next_ptr = ret_ptr->next;
// 再次比较之前获取的栈顶指针ret_ptr和当前的栈顶指针top_ptr
// 如果二者相等,则说明这段时间栈没有发生变化,可以操作,
// 即修改栈顶指针top_ptr为next_ptr
if (top_ptr.compare_exchange_weak(ret_ptr, next_ptr)) {
return ret_ptr;
}
// The stack has changed, start over.
}
}
//
// Pushes the object specified by obj_ptr to stack.
//
void Push(Obj* obj_ptr) {
while(1) {
// 获取栈顶指针,赋值给next_ptr
Obj* next_ptr = top_ptr;
// 将opj_ptr的next指针指向栈顶next_ptr
obj_ptr->next = next_ptr;
// 在此比较之前获取的栈顶指针next_ptr和当前的栈顶top_ptr,
// 如果二者相等,则说明这段时间栈没有发生变化,可以操作,
// 即修改栈顶指针top_ptr为next_ptr
if (top_ptr.compare_exchange_weak(next_ptr, obj_ptr)) {
return;
}
// The stack has changed, start over.
}
}
};
上面就是一个典型的通过CAS loop实现的lock free stack,试想如下场景:
假设当前stack是top->A -> B -> C,线程1在执行Pop操作,当它在最后一步compare_exchange_weak前被抢占挂起,此时线程2执行了下面一系列操作:
POP // 弹出A
POP // 弹出B
delete B
PUSH A // 重新压入A
之后当前的栈变成top->A->C,接着线程A继续执行,在compare_exchange_weak是比较之前获取的栈顶ret_ptr和当前栈顶top_ptr,发现相等(都是A),所以将栈顶top_ptr改成了之前获取的到next_ptr(B),然后返回。
注意,这里栈变成了top->B->C, 然而B已经被线程2 delete掉了,所以会出现各种未定义的问题,导致ABA Problem。这个问题MySQL使用的是version pointer来解决,具体实现下面会说
3. LF_PINS
无锁编程当中要解决的一个重要问题就是:
由于指针都是线程间共享的,当一个线程准备释放一个指针指向的内存时,它无法知道是否另有别的线程也同时持有该块内存的指针并需要访问
那这个问题该如何解决呢,MySQL使用LF_PINS来做(感觉其实就是Hazard Pointer),每个线程从全局的LF_PINBOX中拿到一个LF_PINS, 当使用某个指针PTR之前,先将其赋值给LOCAL_PTR,然后再将PTR pin到自己的LF_PINS当中:
do
{
LOCAL_PTR= PTR;
pin(PTR, PIN_NUMBER);
} while (LOCAL_PTR != PTR)
之后就可以使用LOCAL_PTR并确保其指向的地址肯定不会被其他线程free,因为当其他线程想free某个指针的时候,它会扫描LF_PINBOX中所有LF_PINS,看是否有其他线程已经pin住了相同的地址,如果有的话则不能free
为什么要用do-while来pin呢,是为了确保pin住的PTR和之前取到的LOCAL_PTR是相等的,就是double check下来确保从获取PTR到pin住之间的这段时间,这个指针没有被free,不然假设:
线程1:LOCAL_PTR = PTR
线程2:free(PTR);PTR = 0
线程1:pin(PTR,PIN_NUMBER)
这样的顺序,线程1pin住的PTR是0,其之后要使用的LOCAL_PTR就指向已经被free的地址,会出问题。
看代码:
struct LF_PINS {
// 一个LF_PINS可以同时pin住4个(LF_PINBOX_PINS)个地址
std::atomic<void *> pin[LF_PINBOX_PINS];
// 指向LF_PINBOX
LF_PINBOX *pinbox;
void *purgatory;
uint32 purgatory_count;
std::atomic<uint32> link;
/* we want sizeof(LF_PINS) to be 64 to avoid false sharing */
#if SIZEOF_INT * 2 + SIZEOF_CHARP * (LF_PINBOX_PINS + 2) != 64
char pad[64 - sizeof(uint32) * 2 - sizeof(void *) * (LF_PINBOX_PINS + 2)];
#endif
};
一个LF_PINS中pin住的指针放在pin[LF_PINBOX_PINS]中,最多同时pin住4个,purgatory则是一个类似回收站的链表,当调用
void lf_pinbox_free(LF_PINS *pins, void *addr) {
add_to_purgatory(pins, addr);
if (pins->purgatory_count % LF_PURGATORY_SIZE == 0) {
lf_pinbox_real_free(pins);
}
}
来尝试free指针addr的时,首先会将addr加入到LF_PINS的purgatory链表当中,直到链表当中的元素数LF_PURGATROY_SIZE(10)个时,才真正调用lf_pinbox_real_free来扫描比较LF_PINBOX中所有LF_PINS看addr是否被其他LF_PINS占用,没有的话才可以释放,所以引入purgatory是为了尽可能的减少这样全局扫描的开销。
4. LF_PINBOX
LF_PINBOX是用来管理所有的LF_PINS的,所有线程都从它里面申请一个LF_PINS使用,用完之后再放回来。看下定义:
typedef struct {
LF_DYNARRAY pinarray;
lf_pinbox_free_func *free_func;
void *free_func_arg;
uint free_ptr_offset;
std::atomic<uint32> pinstack_top_ver; /* this is a versioned pointer */
std::atomic<uint32> pins_in_array; /* number of elements in array */
} LF_PINBOX;
pinarray是一个LF_DYNARRAY,最多64k个元素,每个元素都是一个LF_PINS,pins_in_array这是当前数组的大小,所有已回收的LF_PINS还是在数组中,不过使用stack来管理,pinstack_top_ver就是这个栈顶。前面说每个LF_PINS都有一个purgatory链表,链表中每个元素的next指针实际上是在addr的指定偏移位置,这个位置即由free_ptr_offset指定,free_func和free_func_arg则是当某个LF_PINS的purgatory等于10时,真正释放他们的回调函数及参数。
下面看一个申请LF_PINS的函数实现:
LF_PINS *lf_pinbox_get_pins(LF_PINBOX *pinbox) {
uint32 pins, next, top_ver;
LF_PINS *el;
/*
We have an array of max. 64k elements.
The highest index currently allocated is pinbox->pins_in_array.
Freed elements are in a lifo stack, pinstack_top_ver.
pinstack_top_ver is 32 bits; 16 low bits are the index in the
array, to the first element of the list. 16 high bits are a version
(every time the 16 low bits are updated, the 16 high bits are
incremented). Versioning prevents the ABA problem.
*/
// 先检查free stack中是否有之前别的线程还回来的
top_ver = pinbox->pinstack_top_ver;
do {
// 因为pinbox->pinarray最多64K个元素,而pinbox->pinstack_top_ver是32bit,
// 所以他只有低16位是真正的stack top idx,高16位是version
// 所以这里给top_ver取模LF_PINBOX_MAX_PINS便可以拿到stack top idx
if (!(pins = top_ver % LF_PINBOX_MAX_PINS)) {
/* the stack of free elements is empty */
// 如果stack top index为0代表当前free stack里没有,则扩展pinbox->pinarray
// 的元素个数,加1,取一个新的位置
pins = pinbox->pins_in_array.fetch_add(1) + 1;
if (unlikely(pins >= LF_PINBOX_MAX_PINS)) {
return 0;
}
/*
note that the first allocated element has index 1 (pins==1).
index 0 is reserved to mean "NULL pointer"
*/
拿到新位置对应在pinbox->pins_in_array中的元素地址
el = (LF_PINS *)lf_dynarray_lvalue(&pinbox->pinarray, pins);
if (unlikely(!el)) {
return 0;
}
break;
}
// 如果free stack里有元素,则弹出top位置的元素
el = (LF_PINS *)lf_dynarray_value(&pinbox->pinarray, pins);
next = el->link;
// CAS更新pinbox->pinstack_top_ver,后面+LF_PINBOX_MAX_PINS是为了
// 更新前16位的version,这样,每次修改top位置之后,其version都会加1,然后
// 在CAS中同时比较top idx和version来避免ABA问题
} while (!atomic_compare_exchange_strong(
&pinbox->pinstack_top_ver, &top_ver,
top_ver - pins + next + LF_PINBOX_MAX_PINS));
/*
set el->link to the index of el in the dynarray (el->link has two usages:
- if element is allocated, it's its own index
- if element is free, it's its next element in the free stack
*/
// 当LF_PINS分配出去的时候,其link指向的是自己在pinbox->pins_in_array
// 中的index
// 当LF_PINS被还回来push到free stack中时,其link指向的是next element
el->link = pins;
el->purgatory_count = 0;
el->pinbox = pinbox;
return el;
}
pinbox->pinstack_top_ver的高16位是version,每次更新低16位(top index)时,都会将version+1,这样就可以解决前面提到的ABA问题,即使线程2 POP完A,B之后重新压入A,当线程1挂起后重新执行时,虽然看到的栈顶还是A,但当前top index的version已经被线程2加1,所以线程1在之后的CAS中会发现不一致然后重试。
前面说过lf_pinbox_free是先放入到purgatory中,攒够10个再调用lf_pinbox_real_free来真正的free:
void lf_pinbox_free(LF_PINS *pins, void *addr) {
add_to_purgatory(pins, addr);
if (pins->purgatory_count % LF_PURGATORY_SIZE == 0) {
lf_pinbox_real_free(pins);
}
}
/*
Scan the purgatory and free everything that can be freed
*/
static void lf_pinbox_real_free(LF_PINS *pins) {
LF_PINBOX *pinbox = pins->pinbox;
/* Store info about current purgatory. */
struct st_match_and_save_arg arg = {pins, pinbox, pins->purgatory};
/* Reset purgatory. */
// 这里重置pins->purgator,因为在下面的lf_dynarray_iterate中,会将
// 被其他LF_PINS占用的addr重新add到purgatory中
pins->purgatory = NULL;
pins->purgatory_count = 0;
// 遍历pinbox->pinarray中的每个LF_PINS,在match_and_save当中将
// pins->purgatory中的每个addr与每个LF_PINS上pin的所有的地址作比较
// 如果有其他LF_PINS占用,则重新放回到新的purgatory中
lf_dynarray_iterate(&pinbox->pinarray, match_and_save, &arg);
// 此时old_purgatory中放的都是没有被其他LF_PINS占用的地址,可以free
if (arg.old_purgatory) {
/* Some objects in the old purgatory were not pinned, free them. */
void *last = arg.old_purgatory;
while (pnext_node(pinbox, last)) {
last = pnext_node(pinbox, last);
}
// 调用回调函数释放arg.old_purgatory上的所有地址
pinbox->free_func(arg.old_purgatory, last, pinbox->free_func_arg);
}
}
5. LF_ALLOCATOR
LF_ALLOCATOR是一个简易的内存分配器,它里面包含一个LF_PINBOX,所有线程首先先从pinbox中申请一个LF_PINS,然后需要申请内存时就向LF_ALLOCATOR来申请(每次申请的大小固定),将申请到的地址pin在自己的LF_PINS当中。LF_ALLOCATOR将线程free掉的内存同样是用free stack来缓存起来,先看定义:
struct LF_ALLOCATOR {
LF_PINBOX pinbox;
// free stack 的top地址
std::atomic<uchar *> top;
// 每次申请的内存大小
uint element_size;
// 每次执行my_malloc向系统申请内存时加1
// 记录一共向系统申请过多少次内存
std::atomic<uint32> mallocs;
// 从系统申请到内存之后回调constructor
lf_allocator_func *constructor; /* called, when an object is malloc()'ed */
// LF_ALLOCATOR destory遍历已缓存的内存块回调
// destructor
lf_allocator_func *destructor; /* called, when an object is free()'d */
};
下面来看下申请内存的函数:
/*
Allocate and return an new object.
DESCRIPTION
Pop an unused object from the stack or malloc it is the stack is empty.
pin[0] is used, it's removed on return.
*/
// 线程在使用lf_alloc_new之前,需要先调用lf_pinbox_get_pins从LF_ALLOCATOR的pinbox
// 中申请一个LF_PINS,然后每次申请内存前,将其LF_PINS地址传入
void *lf_alloc_new(LF_PINS *pins) {
LF_ALLOCATOR *allocator = (LF_ALLOCATOR *)(pins->pinbox->free_func_arg);
uchar *node;
for (;;) {
// 先看allocator的free stack里是否有缓存
do {
node = allocator->top;
// 有,将其地址赋值给local_ptr node,然后pin住
lf_pin(pins, 0, node);
} while (node != allocator->top && LF_BACKOFF);
// free stack为空,需要向系统申请一块内存
if (!node) {
node = static_cast<uchar *>(
my_malloc(key_memory_lf_node, allocator->element_size, MYF(MY_WME)));
// 申请好之后回调constructor来初始化这块内存
if (allocator->constructor) {
allocator->constructor(node);
}
#ifdef MY_LF_EXTRA_DEBUG
if (likely(node != 0)) {
++allocator->mallocs;
}
#endif
break;
}
if (atomic_compare_exchange_strong(&allocator->top, &node,
anext_node(node).load())) {
break;
}
}
// unpin前面的node
lf_unpin(pins, 0);
return node;
}
可以看到上面有使用LF_PINS来解决在获取top元素之后,更新top时,元素地址被其他线程释放的问题。
不过这里同样是Stack pop操作,没有了version,貌似还是会有ABA问题???
最后再看下LF_ALLOCATOR的destory函数:
void lf_alloc_destroy(LF_ALLOCATOR *allocator) {
uchar *node = allocator->top;
// 首先遍历free stack,回调destructor来释放缓存的内存
while (node) {
uchar *tmp = anext_node(node);
if (allocator->destructor) {
allocator->destructor(node);
}
my_free(node);
node = tmp;
}
// 接着destory pinbox,它实际是一个LF_DYNARRAY,所以
// 会调用lf_dynarray_destroy来释放数组
lf_pinbox_destroy(&allocator->pinbox);
allocator->top = 0;
}
6. 总结
这里有个疑问,无论是LF_PINBOX还是LF_ALLOCATOR,它们的free stack里的元素都不会被free(直到destroy时才会free),所以感觉没必要使用LF_PINS,因为类似Hazard Pointer要解决的问题这里实际是遇不到的,多此一举?倒是LF_ALLOCATOR在pop stack的时候并没有使用version,所以ABA Problem没有被避免?
最近在这里跑出来过不稳定的memory leak,得再好好看下这里的逻辑是否有问题。